Our students have been involved in new and exciting interdisciplinary research and have published in leading high impact journals including Nature Chemistry, Nature Communications, JACS, Angewandte Chemie, Applied Physics Letters, ACS Nano, Nano Letters, Advanced Materials, Nature Protocols, PloS one, and many others.
A full list of the work published by our NanoDTC Students, Associates and others, acknowledging the NanoDTC grants EP/G037221, EP/L015978 and EP/S022953/1 is below. If you want to view the papers on google scholar, see here.
Some papers published by our students are also featured below with some additional contextual information.
Last updated: Mar 2021
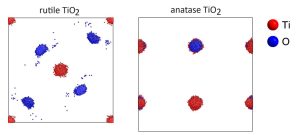
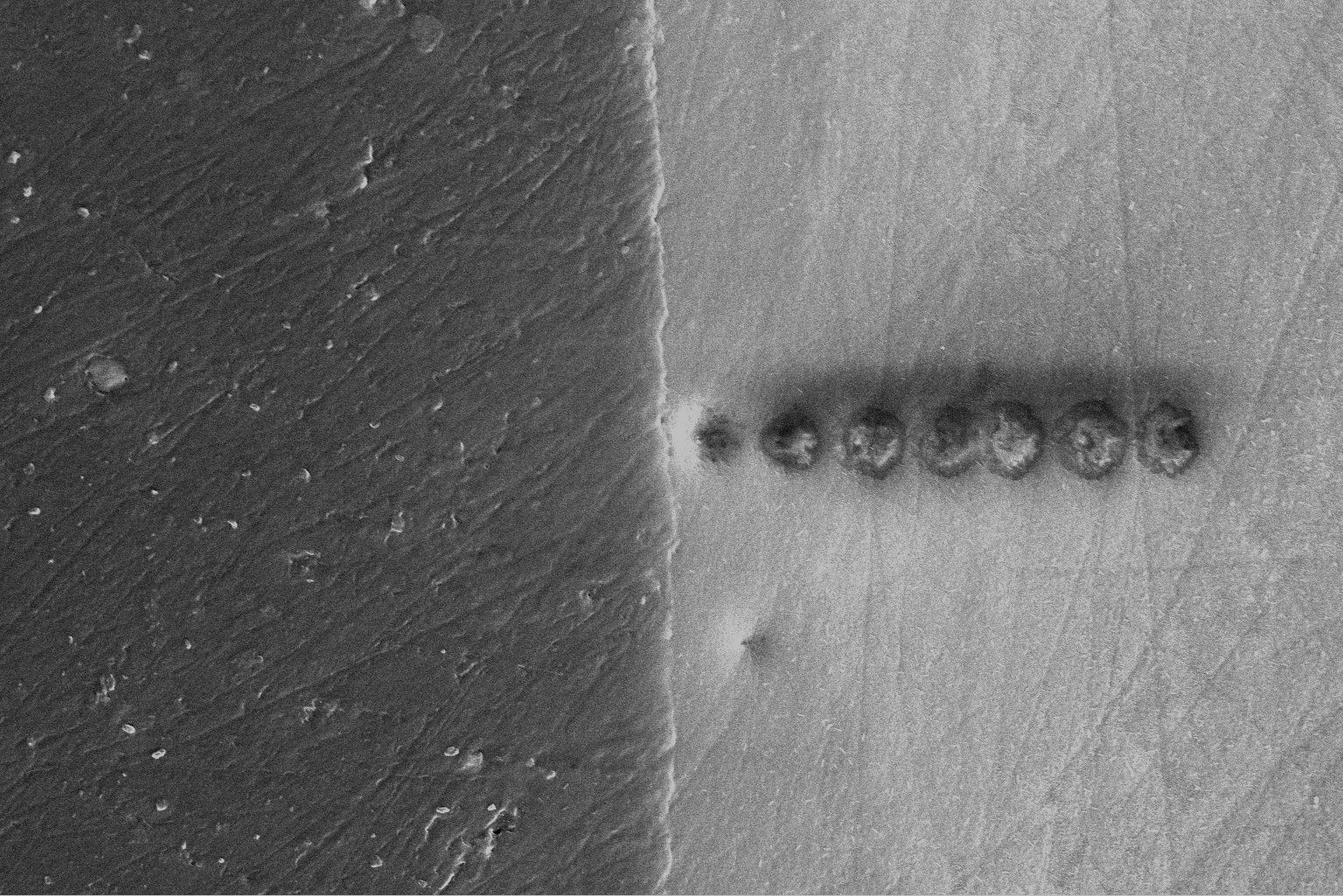
RMCProfile7: reverse Monte Carlo for multiphase systems
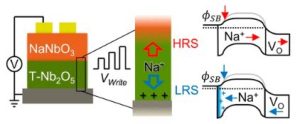
Sodium-Controlled Interfacial Resistive Switching in Thin Film Niobium Oxide for Neuromorphic Applications
Looking inside lithium-ion batteries
Spectroscopy and Electrocatalysis for a Sustainable Future

From waste to fuel: quantifying sustainability
Novel spin states discovered in silicon-based artificial atoms
2016

Holtzmann, Kathrin; Gautier, Hél`ene OB; Christ, Andreas F; Guck, Jochen; Káradóttir, Ragnhildur Thóra; Franze, Kristian
Brain tissue stiffness is a sensitive marker for acidosis Journal Article
In: Journal of neuroscience methods, vol. 271, pp. 50–54, 2016.
@article{holtzmann2016brain,
title = {Brain tissue stiffness is a sensitive marker for acidosis},
author = {Kathrin Holtzmann and Hél{`e}ne OB Gautier and Andreas F Christ and Jochen Guck and Ragnhildur Thóra Káradóttir and Kristian Franze},
url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0165027016301558},
year = {2016},
date = {2016-01-01},
journal = {Journal of neuroscience methods},
volume = {271},
pages = {50--54},
publisher = {Elsevier},
abstract = {Carbon dioxide overdose is frequently used to cull rodents for tissue harvesting. However, this treatment may lead to respiratory acidosis, which potentially could change the properties of the investigated tissue.
},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}

Laura E Ratcliff Edward Tait, Mike Payne; Hine, Nicholas D M
Simulation of electron energy loss spectra of nanomaterials with linear-scaling density functional theory Journal Article
In: Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, vol. 28, no. 19, pp. 195202, 2016.
@article{tait2016simulation,
title = {Simulation of electron energy loss spectra of nanomaterials with linear-scaling density functional theory},
author = {Edward Tait, Laura E Ratcliff, Mike Payne, Peter D Haynes and Nicholas D M Hine},
url = {https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/0953-8984/28/19/195202/meta},
year = {2016},
date = {2016-01-01},
journal = {Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter},
volume = {28},
number = {19},
pages = {195202},
publisher = {IOP Publishing},
abstract = {Experimental techniques for electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS) combine high energy resolution with high spatial resolution. They are therefore powerful tools for investigating the local electronic structure of complex systems such as nanostructures, interfaces and even individual defects. Interpretation of experimental electron energy loss spectra is often challenging and can require theoretical modelling of candidate structures, which themselves may be large and complex, beyond the capabilities of traditional cubic-scaling density functional theory. In this work, we present functionality to compute electron energy loss spectra within the onetep linear-scaling density functional theory code. We first demonstrate that simulated spectra agree with those computed using conventional plane wave pseudopotential methods to a high degree of precision. The ability of onetep to tackle large problems is then exploited to investigate convergence of spectra with respect to supercell size. Finally, we apply the novel functionality to a study of the electron energy loss spectra of defects on the (1 0 1) surface of an anatase slab and determine concentrations of defects which might be experimentally detectable.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}

Michan, Alison L; Divitini, Giorgio; Pell, Andrew J; Leskes, Michal; Ducati, Caterina; Grey, Clare P
Solid electrolyte interphase growth and capacity loss in silicon electrodes Journal Article
In: Journal of the American Chemical Society, vol. 138, no. 25, pp. 7918–7931, 2016.
@article{michan2016solid,
title = {Solid electrolyte interphase growth and capacity loss in silicon electrodes},
author = {Alison L Michan and Giorgio Divitini and Andrew J Pell and Michal Leskes and Caterina Ducati and Clare P Grey},
url = {https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jacs.6b02882},
year = {2016},
date = {2016-01-01},
journal = {Journal of the American Chemical Society},
volume = {138},
number = {25},
pages = {7918--7931},
publisher = {American Chemical Society},
abstract = {The solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) of the high capacity anode material Si is monitored over multiple electrochemical cycles by 7Li, 19F, and 13C solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopies, with the organics dominating the SEI. Homonuclear correlation experiments are used to identify the organic fragments −OCH2CH2O–, −OCH2CH2–, −OCH2CH3, and −CH2CH3 contained in both oligomeric species and lithium semicarbonates ROCO2Li, RCO2Li. The SEI growth is correlated with increasing electrode tortuosity by using focused ion beam and scanning electron microscopy. A two-stage model for lithiation capacity loss is developed: initially, the lithiation capacity steadily decreases, Li+ is irreversibly consumed at a steady rate, and pronounced SEI growth is seen. Later, below 50% of the initial lithiation capacity, less Si is (de)lithiated resulting in less volume expansion and contraction; the rate of Li+ being irreversibly consumed declines, and the Si SEI thickness stabilizes. The decreasing lithiation capacity is primarily attributed to kinetics, the increased electrode tortuousity severely limiting Li+ ion diffusion through the bulk of the electrode. The resulting changes in the lithiation processes seen in the electrochemical capacity curves are ascribed to non-uniform lithiation, the reaction commencing near the separator/on the surface of the particles.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
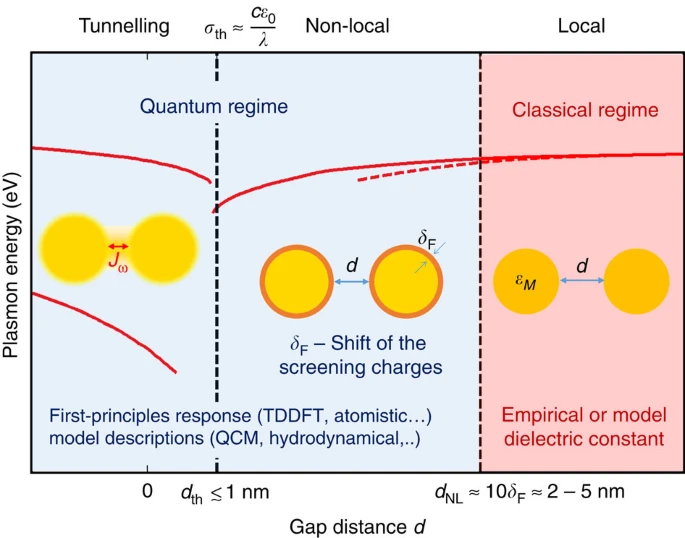
Zhu, Wenqi; Esteban, Ruben; Borisov, Andrei G; Baumberg, Jeremy J; Nordlander, Peter; Lezec, Henri J; Aizpurua, Javier; Crozier, Kenneth B
Quantum mechanical effects in plasmonic structures with subnanometre gaps Journal Article
In: Nature communications, vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 1–14, 2016.
@article{zhu2016quantum,
title = {Quantum mechanical effects in plasmonic structures with subnanometre gaps},
author = {Wenqi Zhu and Ruben Esteban and Andrei G Borisov and Jeremy J Baumberg and Peter Nordlander and Henri J Lezec and Javier Aizpurua and Kenneth B Crozier},
url = {https://www.nature.com/articles/ncomms11495/briefing/signup/},
year = {2016},
date = {2016-01-01},
journal = {Nature communications},
volume = {7},
number = {1},
pages = {1--14},
publisher = {Nature Publishing Group},
abstract = {Metallic structures with nanogap features have proven highly effective as building blocks for plasmonic systems, as they can provide a wide tuning range of operating frequencies and large near-field enhancements. Recent work has shown that quantum mechanical effects such as electron tunnelling and nonlocal screening become important as the gap distances approach the subnanometre length-scale. Such quantum effects challenge the classical picture of nanogap plasmons and have stimulated a number of theoretical and experimental studies. This review outlines the findings of many groups into quantum mechanical effects in nanogap plasmons, and discusses outstanding challenges and future directions.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Li, Guangru; Wisnivesky-Rocca-Rivarola, Florencia; Davis, Nathaniel JLK; Bai, Sai; Jellicoe, Tom C; de la Pe na, Francisco; Hou, Shaocong; Ducati, Caterina; Gao, Feng; Friend, Richard H; others,
Research data supporting "Highly-Efficient Perovskite Nanocrystal Light-Emitting Diodes Enabled by a Universal Cross-linking Method" Journal Article
In: 2016.
@article{li2016research,
title = {Research data supporting "Highly-Efficient Perovskite Nanocrystal Light-Emitting Diodes Enabled by a Universal Cross-linking Method"},
author = {Guangru Li and Florencia Wisnivesky-Rocca-Rivarola and Nathaniel JLK Davis and Sai Bai and Tom C Jellicoe and Francisco de la Pe{~n}a and Shaocong Hou and Caterina Ducati and Feng Gao and Richard H Friend and others},
url = {https://aspace.repository.cam.ac.uk/handle/1810/253968},
year = {2016},
date = {2016-01-01},
publisher = {University of Cambridge},
abstract = {The data corresponds to the images in the paper, the user need to have a power point and an origin software, and then open the data by clicking the images in the powerpoint.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Khan, Ammar A; Rughoobur, Girish; Kamarudin, Muhammad A; Sepe, Alessandro; Dolan, James A; Flewitt, Andrew J; Qasim, Malik M; Wilkinson, Timothy D
Research data supporting "Homologous binary mixtures and improved hole conduction of self-assembled discotic liquid crystals" Journal Article
In: 2016.
@article{khan2016research,
title = {Research data supporting "Homologous binary mixtures and improved hole conduction of self-assembled discotic liquid crystals"},
author = {Ammar A Khan and Girish Rughoobur and Muhammad A Kamarudin and Alessandro Sepe and James A Dolan and Andrew J Flewitt and Malik M Qasim and Timothy D Wilkinson},
url = {https://www.repository.cam.ac.uk/handle/1810/256563},
year = {2016},
date = {2016-01-01},
publisher = {University of Cambridge},
abstract = {Raw data, corresponding to each figure in the paper has been included. This includes data of all the various characterizations that were performed during the research. Excel files summarizing each figure have been included.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}

Li, Guangru; Rivarola, Florencia Wisnivesky Rocca; Davis, Nathaniel JLK; Bai, Sai; Jellicoe, Tom C; de la Pe na, Francisco; Hou, Shaocong; Ducati, Caterina; Gao, Feng; Friend, Richard H; others,
Highly efficient perovskite nanocrystal light-emitting diodes enabled by a universal crosslinking method Journal Article
In: Advanced materials, vol. 28, no. 18, pp. 3528–3534, 2016.
@article{li2016highly,
title = {Highly efficient perovskite nanocrystal light-emitting diodes enabled by a universal crosslinking method},
author = {Guangru Li and Florencia Wisnivesky Rocca Rivarola and Nathaniel JLK Davis and Sai Bai and Tom C Jellicoe and Francisco de la Pe{~n}a and Shaocong Hou and Caterina Ducati and Feng Gao and Richard H Friend and others},
url = {https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/adma.201600064},
year = {2016},
date = {2016-01-01},
journal = {Advanced materials},
volume = {28},
number = {18},
pages = {3528--3534},
abstract = {The preparation of highly efficient perovskite nanocrystal light‐emitting diodes is shown. A new trimethylaluminum vapor‐based crosslinking method to render the nanocrystal films insoluble is applied. The resulting near‐complete nanocrystal film coverage, coupled with the natural confinement of injected charges within the perovskite crystals, facilitates electron–hole capture and give rise to a remarkable electroluminescence yield of 5.7%.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}

Zhao, Qibin; Finlayson, Chris E; Schaefer, Christian G; Spahn, Peter; Gallei, Markus; Herrmann, Lars; Petukhov, Andrei V; Baumberg, Jeremy J
Nanoassembly of polydisperse photonic crystals based on binary and ternary polymer opal alloys Journal Article
In: Advanced Optical Materials, vol. 4, no. 10, pp. 1494–1500, 2016.
@article{zhao2016nanoassembly,
title = {Nanoassembly of polydisperse photonic crystals based on binary and ternary polymer opal alloys},
author = {Qibin Zhao and Chris E Finlayson and Christian G Schaefer and Peter Spahn and Markus Gallei and Lars Herrmann and Andrei V Petukhov and Jeremy J Baumberg},
url = {https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/adom.201600328},
year = {2016},
date = {2016-01-01},
journal = {Advanced Optical Materials},
volume = {4},
number = {10},
pages = {1494--1500},
abstract = {Ordered binary and ternary photonic crystals, composed of different sized polymer‐composite spheres with diameter ratios up to 120%, are generated using bending‐induced oscillatory shearing. This viscoelastic system creates polydisperse equilibrium structures, producing mixed opaline colored films with greatly reduced requirements for particle monodispersity, and very different sphere size ratios compared to other methods of nanoassembly.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
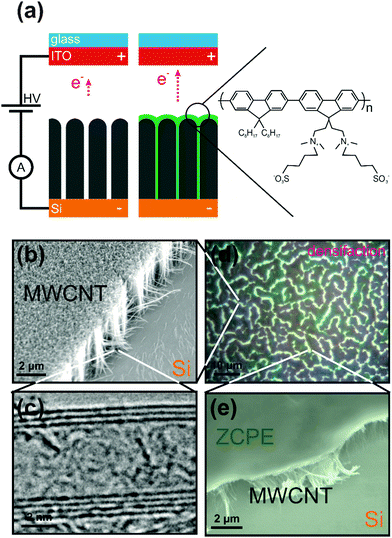
Richard J. Parmee Matthew T. Cole, A Kumar; Milne, William I.
Conjugated polyelectrolyte nano field emission adlayers Journal Article
In: Nanoscale horizons, vol. 1, no. 4, pp. 304–312, 2016.
@article{cole2016conjugated,
title = {Conjugated polyelectrolyte nano field emission adlayers},
author = {Matthew T. Cole, Richard J. Parmee , A Kumar, Clare M Collins, MH Kang, James Xiao, Cinzia Cepek, X Yuan and William I. Milne },
url = {https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlehtml/2016/nh/c6nh00071a},
year = {2016},
date = {2016-01-01},
journal = {Nanoscale horizons},
volume = {1},
number = {4},
pages = {304--312},
publisher = {Royal Society of Chemistry},
abstract = {Here we report on a straightforward and rapid means of enhancing the field electron emission performance of nascent vertically aligned multi-walled carbon nanotubes by introducing a polar zwitterionic conjugated polyelectrolyte adlayer at the vacuum–emitter interface. We attribute the observed 66% decrease in turn-on electric field to the augmented emitter micro-morphology and shifted surface band structure. The composite emitters can be optically modulated by exploiting the absorption cross-section of the solution cast adlayer, which increases the local carrier concentration which broadens the effective electrostatic shape of the emitter during optical excitation. Assessment via scanning anode field emission microscopy reveals a 25% improvement in DC time stability, a significant reduction in long-term hysteresis shift, and a threefold increase in bandwidth during pulsed mode operation.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
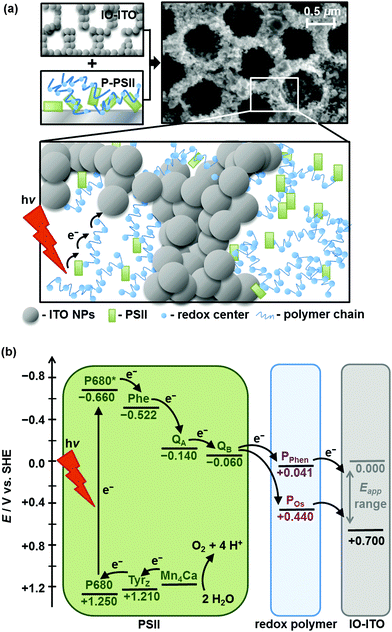
Sokol, Katarzyna P; Mersch, Dirk; Hartmann, Volker; Zhang, Jenny Z; Nowaczyk, Marc M; Rögner, Matthias; Ruff, Adrian; Schuhmann, Wolfgang; Plumeré, Nicolas; Reisner, Erwin
Rational wiring of photosystem II to hierarchical indium tin oxide electrodes using redox polymers Journal Article
In: Energy & Environmental Science, vol. 9, no. 12, pp. 3698–3709, 2016.
@article{sokol2016rational,
title = {Rational wiring of photosystem II to hierarchical indium tin oxide electrodes using redox polymers},
author = {Katarzyna P Sokol and Dirk Mersch and Volker Hartmann and Jenny Z Zhang and Marc M Nowaczyk and Matthias Rögner and Adrian Ruff and Wolfgang Schuhmann and Nicolas Plumeré and Erwin Reisner},
url = {https://pubs.rsc.org/ko/content/articlehtml/2016/ee/c6ee01363e},
year = {2016},
date = {2016-01-01},
journal = {Energy & Environmental Science},
volume = {9},
number = {12},
pages = {3698--3709},
publisher = {Royal Society of Chemistry},
abstract = {Photosystem II (PSII) is a multi-subunit enzyme responsible for solar-driven water oxidation to release O2 and highly reducing electrons during photosynthesis. The study of PSII in protein film photoelectrochemistry sheds light into its biological function and provides a blueprint for artificial water-splitting systems. However, the integration of macromolecules, such as PSII, into hybrid bio-electrodes is often plagued by poor electrical wiring between the protein guest and the material host. Here, we report a new benchmark PSII–electrode system that combines the efficient wiring afforded by redox-active polymers with the high loading provided by hierarchically-structured inverse opal indium tin oxide (IO-ITO) electrodes. Compared to flat electrodes, the hierarchical IO-ITO electrodes enabled up to an approximately 50-fold increase in the immobilisation of an Os complex-modified and a phenothiazine-modified polymer. When the Os complex-modified polymer is co-adsorbed with PSII on the hierarchical electrodes, photocurrent densities of up to ∼410 μA cm−2 at 0.5 V vs. SHE were observed in the absence of diffusional mediators, demonstrating a substantially improved wiring of PSII to the IO-ITO electrode with the redox polymer. The high photocurrent density allowed for the quantification of O2 evolution, and a Faradaic efficiency of 85 ± 9% was measured. As such, we have demonstrated a high performing and fully integrated host–guest system with excellent electronic wiring and loading capacity. This assembly strategy may form the basis of all-integrated electrode designs for a wide range of biological and synthetic catalysts.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Bell, Nicholas AW; Keyser, Ulrich F
Direct measurements reveal non-Markovian fluctuations of DNA threading through a solid-state nanopore Journal Article
In: arXiv preprint arXiv:1607.04612, 2016.
@article{bell2016direct,
title = {Direct measurements reveal non-Markovian fluctuations of DNA threading through a solid-state nanopore},
author = {Nicholas AW Bell and Ulrich F Keyser},
url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/1607.04612},
year = {2016},
date = {2016-01-01},
journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:1607.04612},
abstract = {The threading of a polymer chain through a small pore is a classic problem in polymer dynamics and underlies nanopore sensing technology. However important experimental aspects of the polymer motion in a solid-state nanopore, such as an accurate measurement of the velocity variation during translocation, have remained elusive. In this work we analysed the translocation through conical quartz nanopores of a 7 kbp DNA double-strand labelled with six markers equally spaced along its contour. These markers, constructed from DNA hairpins, give direct experimental access to the translocation dynamics. On average we measure a 5% reduction in velocity during the translocation. We also find a striking correlation in velocity fluctuations with a decay constant of 100s of {mu}s. These results shed light on hitherto unresolved problems in the dynamics of DNA translocation and provide guidance for experiments seeking to determine positional information along a DNA strand.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Sokol, Katarzyna P; Mersch, Dirk; Hartmann, Volker; Zhang, Jenny Z; Nowaczyk, Marc; Rögner, Matthias; Ruff, Adrian; Schuhmann, Wolfgang; Plumeré, Nicolas; Reisner, Erwin
Research data supporting "Rational Wiring of Photosystem II to Hierarchical Indium Tin Oxide Electrodes using Redox Polymers" Journal Article
In: 2016.
@article{sokol2016research,
title = {Research data supporting "Rational Wiring of Photosystem II to Hierarchical Indium Tin Oxide Electrodes using Redox Polymers"},
author = {Katarzyna P Sokol and Dirk Mersch and Volker Hartmann and Jenny Z Zhang and Marc Nowaczyk and Matthias Rögner and Adrian Ruff and Wolfgang Schuhmann and Nicolas Plumeré and Erwin Reisner},
url = {https://www.repository.cam.ac.uk/handle/1810/256734},
year = {2016},
date = {2016-01-01},
publisher = {University of Cambridge},
abstract = {Raw Data supporting publication: ' Rational Wiring of Photosystem II to Hierarchical Indium Tin Oxide Electrodes using Redox Polymers},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Tesoro, Salvatore; Göpfrich, K; Kartanas, Tadas; Keyser, Ulrich Felix; Ahnert, Sebastian Edmund
Nondeterministic self-assembly with asymmetric interactions Journal Article
In: Physical Review E, vol. 94, no. 2, pp. 022404, 2016.
@article{tesoro2016nondeterministicb,
title = {Nondeterministic self-assembly with asymmetric interactions},
author = {Salvatore Tesoro and K Göpfrich and Tadas Kartanas and Ulrich Felix Keyser and Sebastian Edmund Ahnert},
url = {https://journals.aps.org/pre/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevE.94.022404},
year = {2016},
date = {2016-01-01},
journal = {Physical Review E},
volume = {94},
number = {2},
pages = {022404},
publisher = {American Physical Society},
abstract = {We investigate general properties of nondeterministic self-assembly with asymmetric interactions, using a computational model and DNA tile assembly experiments. By contrasting symmetric and asymmetric interactions we show that the latter can lead to self-limiting cluster growth. Furthermore, by adjusting the relative abundance of self-assembly particles in a two-particle mixture, we are able to tune the final sizes of these clusters. We show that this is a fundamental property of asymmetric interactions, which has potential applications in bioengineering, and provides insights into the study of diseases caused by protein aggregation.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Morgenstern, Frederik SF; Böhm, Marcus L; Kist, René JP; Sadhanala, Aditya; Gélinas, Simon; Rao, Akshay; Greenham, Neil C
Research data supporting “Charge Generation and Electron Trapping Dynamics in Hybrid Nanocrystal-Polymer Solar Cells” Journal Article
In: 2016.
@article{morgenstern2016research,
title = {Research data supporting “Charge Generation and Electron Trapping Dynamics in Hybrid Nanocrystal-Polymer Solar Cells”},
author = {Frederik SF Morgenstern and Marcus L Böhm and René JP Kist and Aditya Sadhanala and Simon Gélinas and Akshay Rao and Neil C Greenham},
year = {2016},
date = {2016-01-01},
publisher = {University of Cambridge},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}

Angela Demetriadou Jan Mertens, RW Bowman; others,
Tracking optical welding through groove modes in plasmonic nanocavities Journal Article
In: Nano letters, vol. 16, no. 9, pp. 5605–5611, 2016.
@article{mertens2016tracking,
title = {Tracking optical welding through groove modes in plasmonic nanocavities},
author = {Jan Mertens, Angela Demetriadou, RW Bowman, F Benz, M-E Kleemann, Christos Tserkezis, Y Shi, HY Yang, Ortwin Hess, Javier Aizpurua and others},
url = {https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b02164},
year = {2016},
date = {2016-01-01},
journal = {Nano letters},
volume = {16},
number = {9},
pages = {5605--5611},
publisher = {American Chemical Society},
abstract = {We report the light-induced formation of conductive links across nanometer-wide insulating gaps. These are realized by incorporating spacers of molecules or 2D monolayers inside a gold plasmonic nanoparticle-on-mirror (NPoM) geometry. Laser irradiation of individual NPoMs controllably reshapes and tunes the plasmonic system, in some cases forming conductive bridges between particle and substrate, which shorts the nanometer-wide plasmonic gaps geometrically and electronically. Dark-field spectroscopy monitors the bridge formation in situ, revealing strong plasmonic mode mixing dominated by clear anticrossings. Finite difference time domain simulations confirm this spectral evolution, which gives insights into the metal filament formation. A simple analytic cavity model describes the observed plasmonic mode hybridization between tightly confined plasmonic cavity modes and a radiative antenna mode sustained in the NPoM. Our results show how optics can reveal the properties of electrical transport across well-defined metallic nanogaps to study and develop technologies such as resistive memory devices (memristors).},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Dolan, James A; Saba, Matthias; Dehmel, Raphael; Gunkel, Ilja; Gu, Yibei; Wiesner, Ulrich; Hess, Ortwin; Wilkinson, Timothy D; Baumberg, Jeremy J; Steiner, Ullrich; others,
Research Data Supporting" Gyroid Optical Metamaterials: Calculating the Effective Permittivity of Multidomain Samples" Journal Article
In: 2016.
@article{dolan2016research,
title = {Research Data Supporting" Gyroid Optical Metamaterials: Calculating the Effective Permittivity of Multidomain Samples"},
author = {James A Dolan and Matthias Saba and Raphael Dehmel and Ilja Gunkel and Yibei Gu and Ulrich Wiesner and Ortwin Hess and Timothy D Wilkinson and Jeremy J Baumberg and Ullrich Steiner and others},
url = {https://www.repository.cam.ac.uk/bitstream/handle/1810/260150/Description.pdf?sequence=5},
year = {2016},
date = {2016-01-01},
publisher = {University of Cambridge},
abstract = {The data is arranged into three folders (.zip files; bold), each of which contains the follow files (.tif and
.txt files; italics). This data and the descriptions below should be read in conjunction with the manuscript
(particularly the “Experimental Methods” section) and “supporting info”, both of which may be found at
the following DOI: http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acsphotonics.6b00400},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
.txt files; italics). This data and the descriptions below should be read in conjunction with the manuscript
(particularly the “Experimental Methods” section) and “supporting info”, both of which may be found at
the following DOI: http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acsphotonics.6b00400
George, Chandramohan; Morris, Andrew J; Modarres, Mohammad H; Volder, Michael De
In: 2016.
@article{george2016research,
title = {Research data supporting “Structural Evolution of Electrochemically Lithiated MoS2 Nanosheets and the Role of Carbon Additive in Li-Ion Batteries”},
author = {Chandramohan George and Andrew J Morris and Mohammad H Modarres and Michael De Volder},
url = {https://www.repository.cam.ac.uk/handle/1810/260253},
year = {2016},
date = {2016-01-01},
publisher = {University of Cambridge},
abstract = {Crystallographic structure files of materials discovered in the research.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Rivett, Jasmine PH; Richter, Johannes M; Price, Michael B; Credgington, Dan; Deschler, Felix
Carrier-phonon interactions in hybrid halide perovskites probed with ultrafast anisotropy studies Proceedings Article
In: Physical Chemistry of Interfaces and Nanomaterials XV, pp. 99231E, International Society for Optics and Photonics 2016.
@inproceedings{rivett2016carrier,
title = {Carrier-phonon interactions in hybrid halide perovskites probed with ultrafast anisotropy studies},
author = {Jasmine PH Rivett and Johannes M Richter and Michael B Price and Dan Credgington and Felix Deschler},
url = {https://www.spiedigitallibrary.org/conference-proceedings-of-spie/9923/99231E/Carrier-phonon-interactions-in-hybrid-halide-perovskites-probed-with-ultrafast/10.1117/12.2238906.short?sessionGUID=02bc9993-ced2-68be-ad49-a28531ab0d3a&sessionGUID=02bc9993-ced2-68be-ad49-a28531ab0d3a&webSyncID=6ec7a49d-ab6a-0cba-d059-329ad883c9d9&SSO=1},
year = {2016},
date = {2016-01-01},
booktitle = {Physical Chemistry of Interfaces and Nanomaterials XV},
volume = {9923},
pages = {99231E},
organization = {International Society for Optics and Photonics},
abstract = {Hybrid halide perovskites are at the frontier of optoelectronic research due to their excellent semiconductor properties and solution processability. For this reason, much attention has recently been focused on understanding photoexcited charge-carrier generation and recombination in these materials. Conversely, very few studies have so far been devoted to understanding carrier-carrier and carrier-phonon scattering mechanisms in these materials. This is surprising given that carrier scattering mechanisms fundamentally limit charge-carrier motilities and therefore the performance of photovoltaic devices. We apply linear polarization selective transient absorption measurements to polycrystalline CH3NH3PbBr3 hybrid halide perovskite films as an effective way of studying the scattering processes in these materials. Comparison of the photo induced bleach signals obtained when the linear polarizations of the pump and probe are aligned either parallel or perpendicular to one another, reveal a significant difference in spectral intensity and shape within the first few hundred femtoseconds after photoexcitation.
© (2016) COPYRIGHT Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE). Downloading of the abstract is permitted for personal use only.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
© (2016) COPYRIGHT Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE). Downloading of the abstract is permitted for personal use only.

Zhang, Yingbo; Buell, Alexander K; Müller, Thomas; Genst, Erwin De; Benesch, Justin; Dobson, Christopher M; Knowles, Tuomas PJ
Protein Aggregate-Ligand Binding Assays Based on Microfluidic Diffusional Separation Journal Article
In: ChemBioChem, vol. 17, no. 20, pp. 1920–1924, 2016.
@article{zhang2016protein,
title = {Protein Aggregate-Ligand Binding Assays Based on Microfluidic Diffusional Separation},
author = {Yingbo Zhang and Alexander K Buell and Thomas Müller and Erwin De Genst and Justin Benesch and Christopher M Dobson and Tuomas PJ Knowles},
url = {https://chemistry-europe.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/cbic.201600384},
year = {2016},
date = {2016-01-01},
journal = {ChemBioChem},
volume = {17},
number = {20},
pages = {1920--1924},
publisher = {Wiley Online Library},
abstract = {The measurement of molecular interactions with pathological protein aggregates, including amyloid fibrils, is of central importance in the context of the development of diagnostic and therapeutic strategies against protein misfolding disorders. Probing such interactions by conventional methods can, however, be challenging because of the supramolecular nature of protein aggregates, their heterogeneity, and their often dynamic nature. Here we demonstrate that direct measurement of diffusion on a microfluidic platform enables the determination of affinity and kinetics data for ligand binding to amyloid fibrils in solution. This method yields rapid binding information from only microlitres of sample, and is therefore a powerful technique for identifying and characterising molecular species with potential therapeutic or diagnostic application.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Angela Demetriadou Jan Mertens, RW Bowman; others,
Research data supporting “Tracking optical welding through groove modes in plasmonic nano-cavities” Journal Article
In: 2016.
@article{mertens2016research,
title = {Research data supporting “Tracking optical welding through groove modes in plasmonic nano-cavities”},
author = {Jan Mertens, Angela Demetriadou, RW Bowman, F Benz, M-E Kleemann, Christos Tserkezis, Y Shi, HY Yang, Ortwin Hess, Javier Aizpurua and others},
url = {https://www.repository.cam.ac.uk/handle/1810/257368},
year = {2016},
date = {2016-01-01},
publisher = {University of Cambridge},
abstract = {Research data for the manuscript "Tracking optical welding through groove modes in plasmonic nano-cavities" published in Nano Letters},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}